22 A Simple Vaccine Intervention
EpiModel built-in network models also include parameters for a simple intervention that affects the probability of infection given contact between a susceptible and an infected person. This could be, for example, a vaccine that reduces the susceptibility or a condom provision program. This mini-tutorial will show you how to implement such an intervention.
Research-level models would implement more complex interventions with more parameters or greater demographic structure; we’ll discuss that in NME-II.
Interventions in this simple built-in approach have three salient features:
- They apply to everyone in the population. There is no heterogeneity in who gets the intervention.
- The interventions have an efficacy,
inter.eff, where the invention results in a relative reduction in the probability of infection specified ininf.probbyinter.eff. - Interventions start at a defined time step,
inter.start.
To start, we estimate a very simple temporal ERGM.
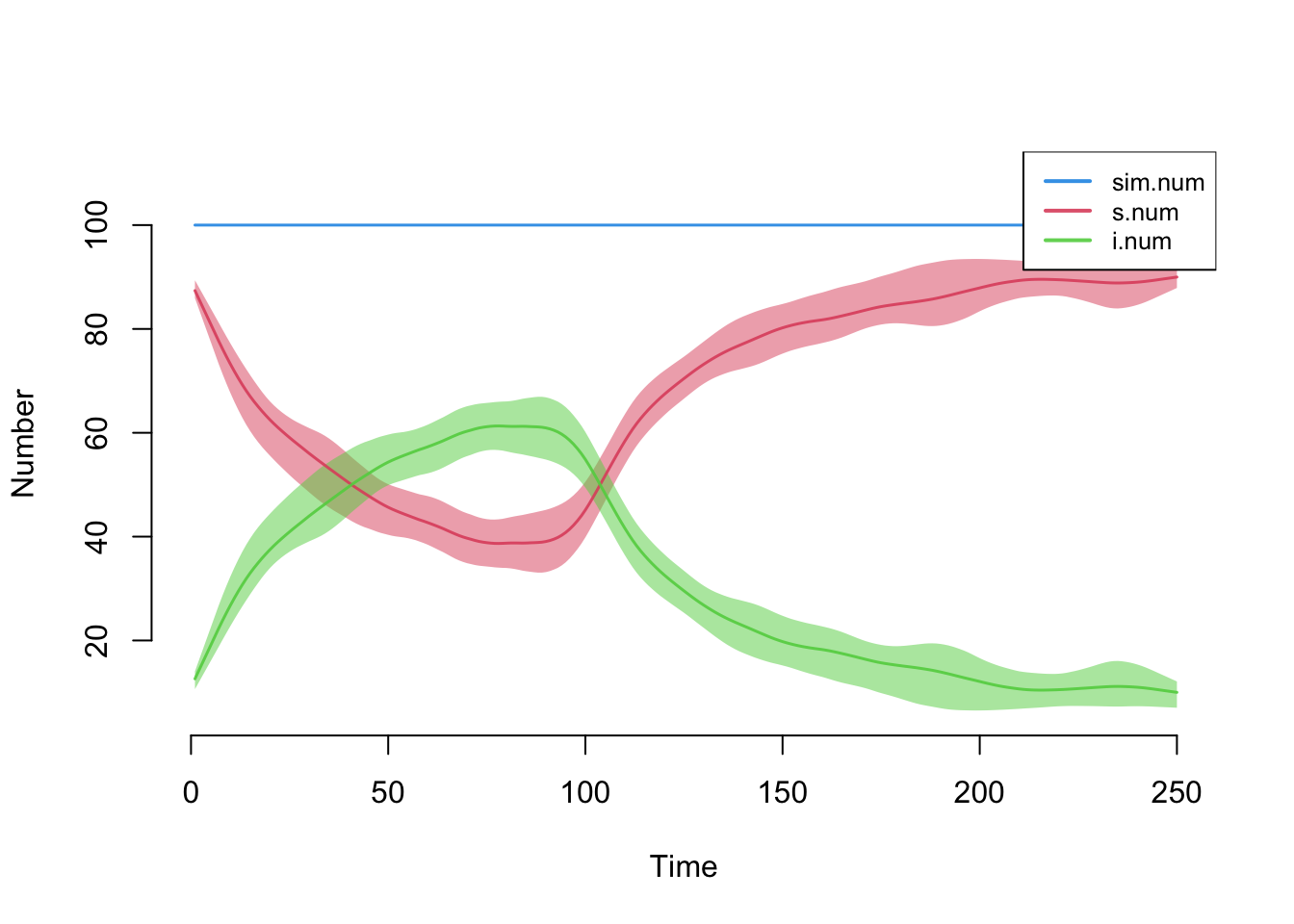
This model simulates an SI disease in a closed population in which the intervention (e.g., a vaccine) has a very strong efficacy for the entire population. The intervention starts at week 25.
Code
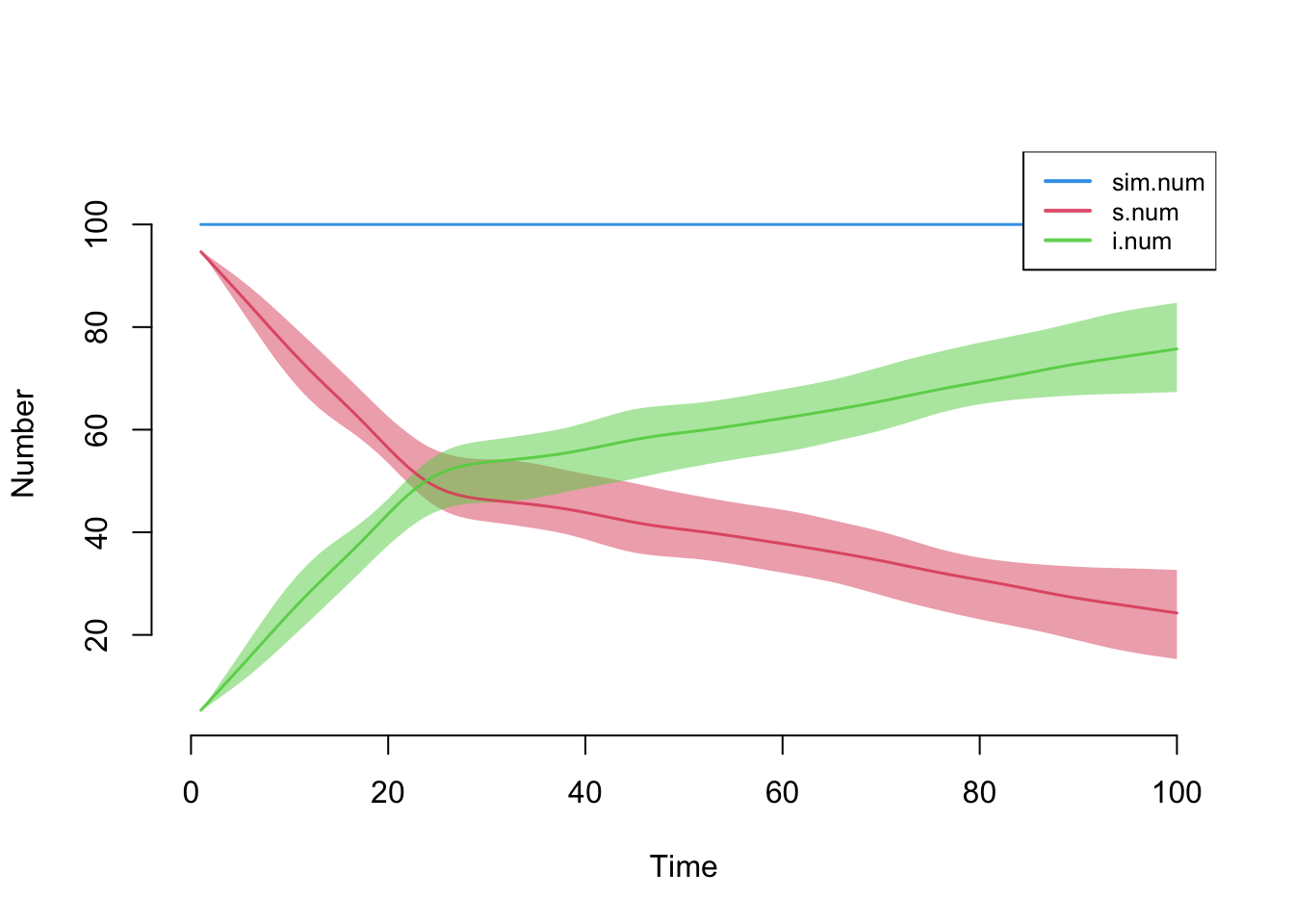
The next model simulates an SIS disease in which the intervention is slightly less effective (e.g., functional effectiveness of condoms) that starts at week 100.